Top Memorization Techniques to Boost Your Learning Power

Have you ever wondered how actors remember their lines? Because a film can have a bunch of them, especially in a Tarantino film! Or, if you joined the Queen’s Gambit hype, how did Beth Harmon memorize all those (im)possible opening moves? Hard! The truth is memorizing information can be tough, especially if you don’t have any memorization techniques at your disposal or a trained memory.
But with the right techniques to memorize, anyone can become better at memorizing facts and figures. At Monitask, we love to help you improve, hop into the II part of our series of the best memory strategies (read part I here) and how you can use them to boost your learning power!

Memorization is a hot topic for scientific endeavors, after all, memory is one of the best commodities of being a human! According to Yingxu Wang, “memorization is a cognitive process of the brain at the meta-cognitive layer that establishes (encodes and retains) and reconstructs (retrieves and decodes) information in long-term memory”
Memorization is a cognitive process that works both ways – save information to memory and retrieve it when you need it

Therefore, if memorization is a process, we have to start somewhere! The first step to good memorization is to understand that memorization techniques are divided into two categories: memorizing facts (think: memorizing numbers) and memorizing ideas or processes (think: memorizing a chess match). For the former, you need repetition and for the latter, conceptual understanding.
Let’s review the process!
The Process of Memorization to Remember Things
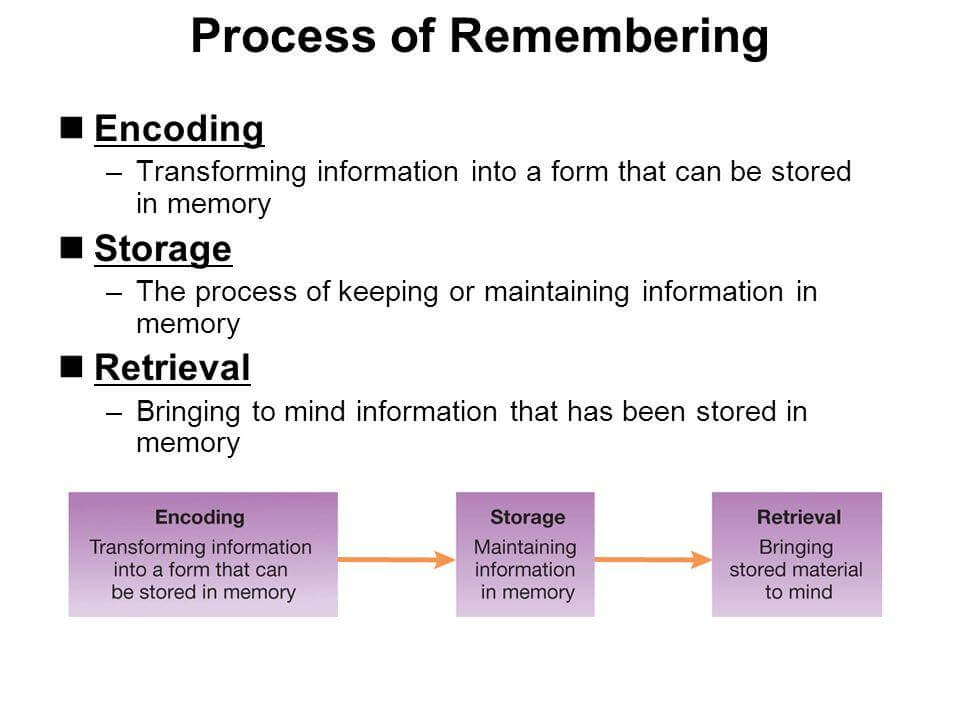
Overall, we can summarize this process in 3 steps:
- Encoding
- Storage
- Retrieval
Encoding
The first step of memorization is to encode the information. This means taking in the information and transforming it into a form that can be stored in memory. To do this, you need to pay attention and focus on what you are trying to memorize.
Next, you will need to use memorization techniques such as mnemonic devices and associations to help encode the information in a format you feel more comfortable with.
Storage
Once you have encoded the information, it needs to be stored in your long-term memory. This is done by repeating and rehearsing the information over time, spaced repetition is a good technique for this. The more you repeat the information, the more likely you are to retain it in memory.
Retrieval
Finally, memorization requires the ability to recall or retrieve information when needed. To do this, you will need to use memorization techniques such as mental imagery and retrieval practice. These memorization techniques help strengthen your memory so that you can quickly access the information when you need it.
In the image below, you can visually learn the process of memorization!
Now that you know the basics, let’s take a look at some other memorization techniques that you can use to boost your learning power!
Top Memorization Techniques to Boost Your Learning Power
In our part I of the memorization techniques series, we covered 9 techniques to memorize information.
- The Loci Technique
- Mnemonics Devices
- Storytelling Technique
- Chunking Technique
- Peg System
- Association Technique
- Spaced Repetition Technique
- Link System
- Rainbow Memory
Let’s review another set of them!
Mind Maps
Mind mapping has quickly become a preferred memorization technique in recent years due to its ability to improve one’s understanding and retention of information. By using mind maps, relationships between thoughts, facts, and ideas can be easily visualized and represented logically.
A Johns Hopkins study indicates that students who use mind mapping increase their grades by 12%
To create an effective mind map, simply write down the main topic at the center of the page. Sub-topics and ideas can then be related to each other connecting lines that are drawn outwards. This creative process helps bring clarity and new insights into abstract topics while increasing comprehension through effective organization of thought.
Below, you have a great example provided by Mind Mapping.
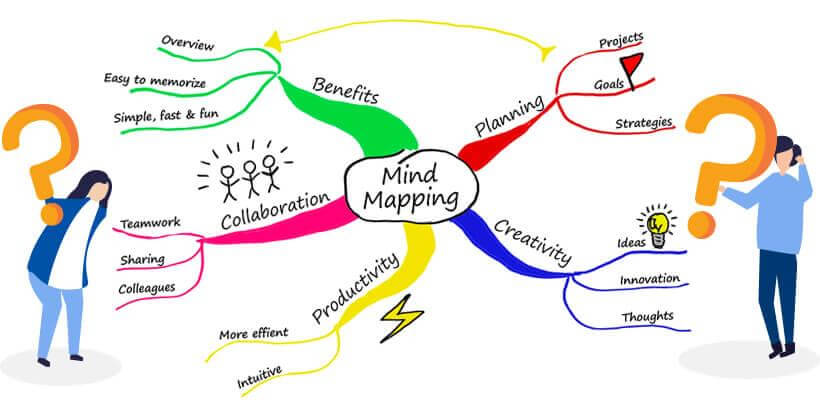
Since mind mapping involves engaging both sides of the brain with visual cues while stimulating rational thinking processes, it has great potential in forming a strong foundation for improved memory capabilities along with a deeper understanding of information.
Rote Learning
Rote memorization, also known as rote learning is a memorization technique that many educational professionals find effective for learning facts, numbers, and formulas. It involves repeating an item repeatedly until it can be recalled from memory without prompt or aid.

Rote memorization plays an especially important role in teaching students how to acquire foreign language skills by sitting through classes that involve the repetition of grammatical structures and vocabulary words.
Other scenarios where this memorization technique can be particularly useful are when memorizing definitions and terms in scientific or technological contexts. Rote memorization also promotes staying focused on a particular task at hand as opposed to being distracted by other sources of information.
Get more out of your business
Get the best employee engagement content every week via mailing list
Flashcards
Flashcards have long been used as a reliable memorization technique, and they are still popular today. Flashcards are versatile in the way they can be used to learn a variety of information, such as language vocabulary, musical notes, scientific systems, and even historical facts. They are also easily transportable in their physical paper or card form making them easy to use on the go.
As flashcards test both knowledge and recall-ability. Making one’s own flashcards is a great way to hone your skill for studying what matters most for you specifically; effective use of flashcards allows you to focus primarily on areas that need more reinforcement so that you can understand complex topics efficiently. This strategy provides an efficient way for revising showing evidence of improved memory retention.
Gamification
Gamification is an effective memorization technique that can be used to help individuals learn and remember new information. Gamification applies principles derived from gaming activities to learning materials, providing users with rewards and incentives which increase engagement and encourage memorization.
According to Zippia, 67% of students choose gamification for their educational experiences over others
Through gamification, learners are incentivized to reach some goal related to the material they are learning. This increases enthusiasm for the activity, promotes motivation, and encourages committed effort, resulting in better retention of information by the learner due to repeated exposure.
Gamification also provides an opportunity to become a superlearner and to practice within a controlled environment until they are comfortable with the concepts being taught. With its fun and engaging approach gamification is fast becoming a popular method for aiding memorization amongst students of all ages.
Active Recall Method of Memorizing
The active recall method is an effective memorization technique that has been used successfully to remember and retain information. This method is based on actively retrieving information from memory rather than passively reviewing facts.
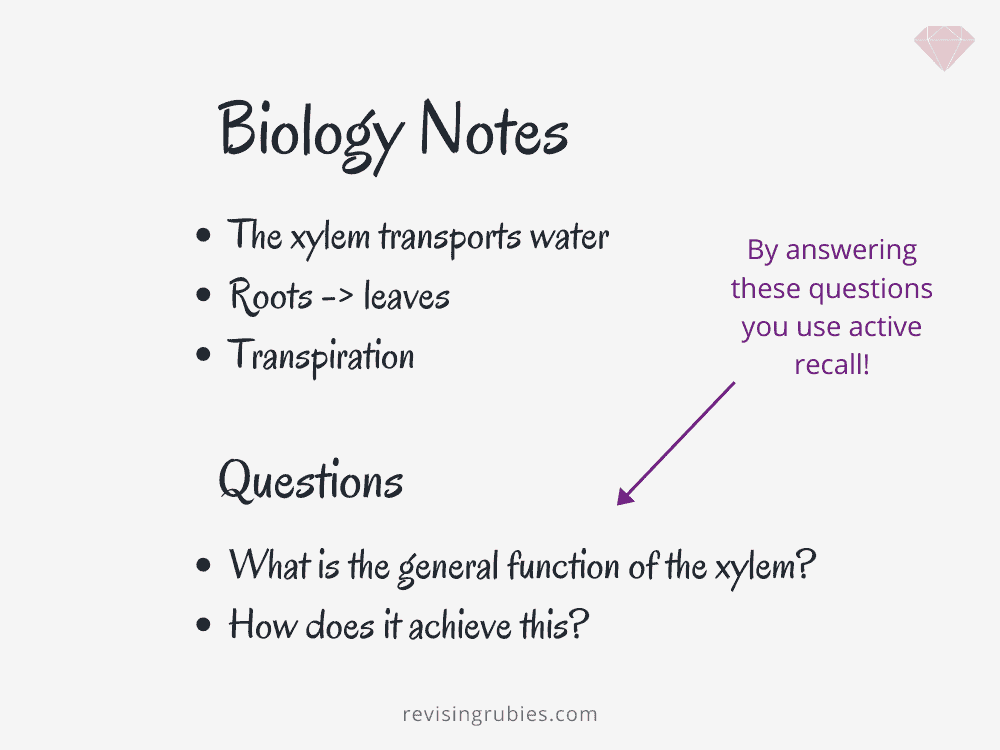
Active recollection can be similar to spaced repetition, but it differs in that it requires recalling information rather than simply re-reading
It is an efficient way to memorize facts and figures as it involves purposefully engaging with the material to solidify the connections between concepts and facts by using repetition and quizzing yourself each time you review it, encouraging your brain to form stronger neural pathways for easier recall later.
Active recall can work for almost any type of fact or content, enabling users to quickly increase their knowledge base without spending a lot of time on it. It can be used both as a learning tool and a study aid as its focused approach helps foster better understanding. When integrated into one’s overall learning routine, active recall can be a powerful ally for mastering difficult topics more quickly–and help make long-term retention effortless.
The Feynman Method
The Feynman Method is an effective memorization technique that has gained popularity in recent years. Named after the influential physicist Richard Feynman, it involves breaking down complex concepts and topics into simpler understandable pieces. This method helps to structure them for easier learning and information retention.
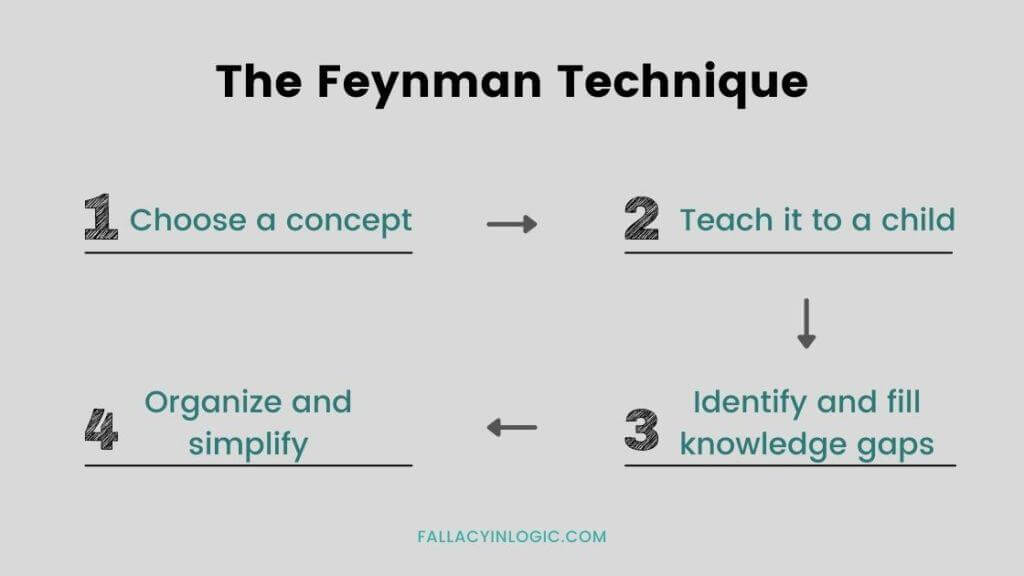
Feynman believed that one should be able to explain a concept simply and clearly in their own words, which can only be done if its understanding runs deep at a fundamental level. A great benefit of the Feynman method is its adaptability.
Its usage isn’t limited to academic or professional fields but can also be used by anyone looking to delve deeper into a particular topic out of curiosity or interest. With practice and dedication, it’s an excellent way for individuals to maximize their understanding and knowledge of any subject area.
The Cognitive Load Theory
Cognitive load theory, or CLT, is a dynamic concept developed by Cognitive Psychologist John Sweller. It has been proven to be a successful technique for aiding and improving memorization skills. Cognitive load theory is a simple yet powerful memorization technique based on the idea that human brains can only process a certain amount of information at one time.
Cognitive load theory helps individuals to more efficiently take in and retain new material by breaking it into manageable chunks. For example, instead of looking at an entire page of text, individuals using cognitive load theory will break the page into smaller pieces, including concepts, ideas, and keywords. Breaking the content into manageable chunks helps reduce cognitive overload and makes it easier to recall the material at a later date.
Instead of looking at an entire page of text, individuals using cognitive load theory will break the page into smaller pieces, including concepts, ideas, and keywords
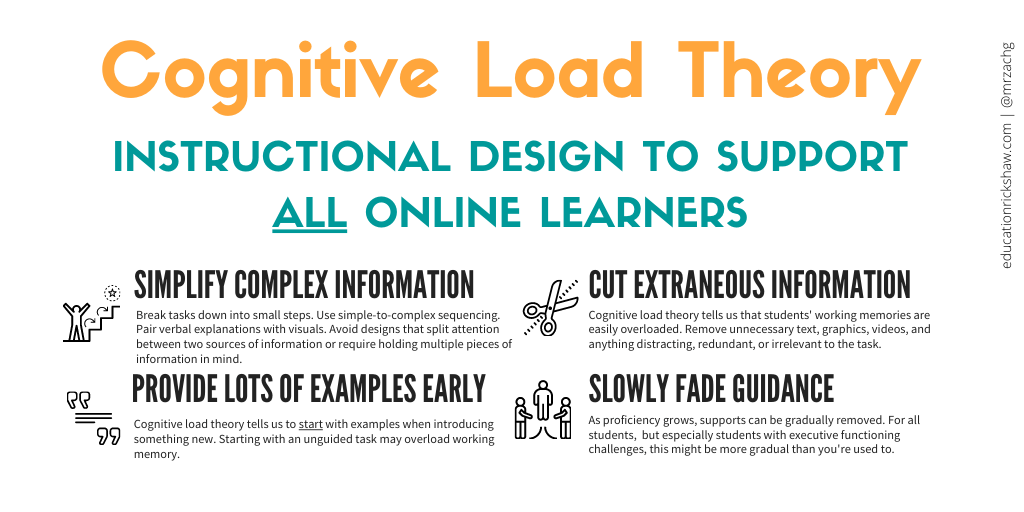
Cognitive load theory is particularly useful when memorizing information for long-term usage such as studying for an exam or preparing a speech. By providing participants with a framework for how best to organize and remember information, cognitive load theory has become an increasingly popular memorization technique that can provide great results in terms of retention and recall of material.
The 5 Whys Method
The 5 Whys Method is a powerful memorization technique known for helping individuals reach a meticulous understanding of complex concepts. The first step of The 5 Why Method is to identify the main premise of what are you learning, then ask “Why did this happen?” The next four steps involve keeping this line of inquiry going until an in-depth conclusion is reached.

This method is incredibly effective in helping people tackle a problem by drilling down to the source and retrieving essential facts that can be committed to memory. The 5 Whys Method not only engages learners through its interactive nature while conducting research.
Also, this method allows learners to pattern their thoughts after observing core relationships between ideas. Memorizing can be difficult, but The 5 Whys Method offers an effective approach with pinpoint accuracy as learners deepen their comprehension abilities.
Maintaining memorization skills is an essential component of any successful educational or professional journey
While there are many memorization techniques available, the ones featured in this article have been proven effective and can help learners from all backgrounds get the most out of their studies.
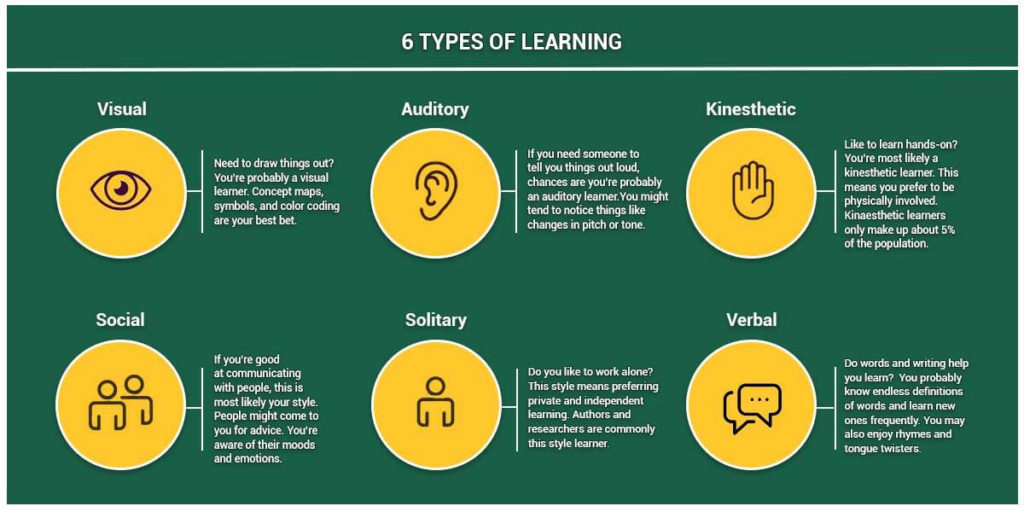
Memorization and Type of Learning
Along with memorization techniques, individuals must also make sure they are engaging in the type of learning that best suits their needs. Overall, there are 6 styles of learning: visual, auditory, kinesthetic, social, solitary, and verbal.
- Visual learning refers to taking in information through pictures, diagrams, and other forms of visuals.
- Auditory learners best comprehend new material by hearing it- from lectures or stories for instance.
- Kinesthetic learning means that students learn by doing physical activities such as experiments, constructing models, and role-playing situations.
- Social learning involves collaborating with others during projects and activities that focus on critical thinking skills.
- Solitary learners have to have individual study time to properly absorb new material and verbal learners rely on discussion and explaining concepts out loud for comprehension.
- Verbal learning involves repeating concepts, phrases, and verbiage out loud so that they become easier to remember.
Which are you?
Memorization techniques coupled with recognition of their learning style will help you maximize your learning potential!
Takeaway
Memorization is one of the most recognized processes to experience life and grasp information. As memorization is such a vital part of learning, being able to effectively memorize information can provide great advantages in many different ways.
Using memorization techniques like Feynman’s Method, Cognitive Load Theory, and The 5 Whys Method can greatly increase memorization skills and allow individuals to unlock their full potential. Each technique has its own strengths and weaknesses, so it’s important to choose the memorization technique that works best for a particular learner.
No matter which memorization method is used, having a strong trained memory can help open up many new opportunities in life and provide more possibilities for future success. Did you like the post? Check our blog post archive here!
-The Monitask Team


