Tips and Ways to Measure Your Project’s Impact

There are a lot of talks these days about impact measurement and how to go about it effectively. Many organizations are looking to measure the impact of their projects to assess whether they are achieving their desired outcomes. But what does it mean to measure project impact, and how do you do it?
In this blog post, we will explore some tips on how to run effective impact measurement projects. We’ll discuss what project impact indicators are, and how impacts can be measured using different types of data. So if you’re wondering how to measure the impact of your project, read on!
When we talk about project impact, we’re referring to the positive or negative outcomes that a project produces. These outcomes can be measured in terms of changes in knowledge, attitudes, behaviors, skills, or any other desired result.
If you are a teacher or a professor, surely you have some measurement methods in place, let them be exams or final projects. As well, if you are a manager, you probably assess your team or project results by looking at the sales, clients’ satisfaction, and so on. We all want to know how well we are coping or where exactly we are failing!
Yet, it’s not a white or black scenario! And, you must know that project impact assessment is not an easy task. Several factors can interfere with the way you will get your results.
The Challenges of Project Impact Measurement
If you type “impact project measurement” on Google scholar, you will get approximately 6,400,000 results in just 0,10 seconds! Yes, this is a very popular topic and, as we can see, there are many ways of measuring impact.
However, project impact measurement can be quite challenging for several reasons.
- First of all, it can be difficult to identify which outcomes are attributable to the project (versus other factors).
- Secondly, data on project outcomes may not be available immediately or may be of poor quality.
- Finally, measuring project impact requires a certain level of resources and expertise.
Despite these challenges, project impact measurement is essential for understanding whether a project is achieving its desired outcomes. Furthermore, impact data can be used to improve project design and implementation. For these reasons, it is important to invest time and resources in project impact measurement.
Why Measure Your Project’s Impact?
There are several reasons why you might want to measure project impact.
As we stated before, impact data can be used to improve project design and implementation. By understanding which project activities lead to desired outcomes, you can make changes to the project (e.g., add or remove activities) to improve its effectiveness.
On the other hand, it helps you to inform decision-making about resource allocation. If a project is shown to be effective, it may be eligible for additional funding. Conversely, if a project is not effective, resources may be redirected to more productive uses.

Third, impact data can help build support for the project among key stakeholders (e.g., funders, government officials). Impactful projects are more likely to receive continued support and funding.
Finally, project impact measurement can help improve accountability and transparency. By measuring project outcomes, project managers can demonstrate to key stakeholders that the project is achieving its intended results.

As you can see, there are many reasons why you might want to measure project impact. In the next section, we will discuss some tips on how to do it.
Get more out of your business
Get the best employee engagement content every week via mailing list
How to Measure Project Impact?
Now that we’ve discussed some of the reasons why you might want to measure project impact, let’s take a look at the process!
Previous Preparation
You can’t start an impact measurement out of anywhere! In your project’s plan, you need to outline what you are trying to change to know how to measure that change. This would correspond to your project’s theory of change. In summary, identify how your project is expected to lead to desired outcomes.
Then, select appropriate indicators for measuring project outcomes
There are many different types of impact indicators (e.g., knowledge, attitudes, behaviors), as well as to identify your target population and baseline data. The target population is the group of people that you expect to be affected by the project. Baseline data are quantitative or qualitative data collected before the project starts.
Below, you can take a look at an example of impact indicators for a social project:
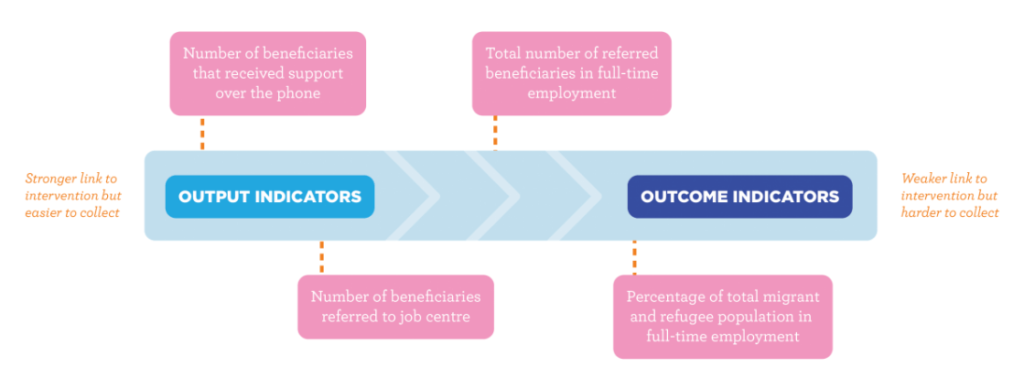
Finally, establish a system for collecting impact data. This includes deciding who will collect data, when data will be collected, and how data will be stored.
- Identify project objectives: What are the project’s goals and objectives?
- Develop project indicators: What data will you collect to measure project outcomes? How will you collect this data?
- Select data collection methods: What qualitative and/or quantitative methods will you use to collect data on project outcomes?
These are the main preparatory steps you need to take before starting your project’s impact measurement!
Identify the Type of Data You Need
Two main types of data can be used to measure project impact:
- Quantitative data: This type of data is typically collected through surveys or other forms of data collection (e.g., focus groups, interviews). It can be used to measure changes in project outcomes (e.g., knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors) over time.
- Qualitative data: This type of data is usually collected through interviews or focus groups. It can be used to understand the project’s impact on participants’ lives (e.g., how the project has affected their relationships, work, and health).
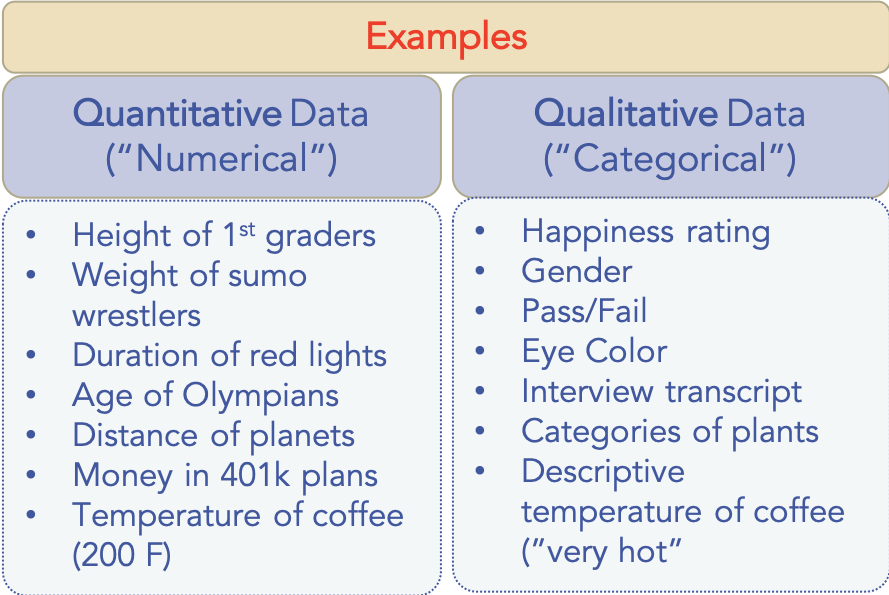
It is important to note that both quantitative and qualitative data are important for understanding project impact. Quantitative data provides a more objective picture of project outcomes, while qualitative data provides a more in-depth understanding of how the project has affected participants’ lives.
In some cases, you may only have one type of data available (e.g., quantitative data from surveys). In other cases, you may have both types of data available. If possible, it is always best to use both types of data to get a more complete picture of the project’s impact.
Data Collection
The next step is to collect data on project outcomes! This can be done through surveys, interviews, focus groups, or other data collection methods.
Surveys
If you are collecting quantitative data, surveys are typically the best method. Surveys can be administered online, by mail, or in person. They can be used to measure changes in project outcomes.
If you are using surveys to collect data, there are a few things to keep in mind:
- Make sure the survey is short and easy to understand. If the survey is too long or confusing, people will be less likely to complete it.
- Make sure the survey questions are clear and concise. Avoid using jargon or technical terms that people may not be familiar with.
- Be sure to pilot the survey before administering it to your target population. This will help you identify any problems with the survey (e.g., unclear questions, confusion about instructions).
Most projects rely heavily on surveys, make sure to use a reputable survey company
SurveyMonkey, an internet program and hosting site that allows you to develop online surveys, gives you an easy-to-follow guideline for creating an effective survey and you can read it here.
Interviews
On the other hand, if you are collecting qualitative data, interviews are typically the best method. Interviews can be conducted in person, by phone, or via video chat. They provide an opportunity for people to share their stories and experiences in their own words.
If you are using interviews to collect data, there are a few things to keep in mind:
- Plan ahead conducting interviews, it is important to have a plan. This includes having a list of questions prepared in advance.
- It can also be helpful to create a guide for the interview, which outlines the topics you want to cover and the order in which you want to cover them.
- Choose interviewees who are representative of your target population.
- Ask open-ended questions that encourage participants to share their experiences and feelings.
Focus Groups
Focus groups are another type of qualitative data collection that involves bringing a group of people together to discuss a particular topic. Focus groups can be used to collect data on project outcomes and understand the project’s impact on participants’ lives.
When conducting focus groups, it is important to:
- Choose participants who are representative of your target population.
- Have a moderator who is skilled in leading discussions and keeping the conversation on track.
- Create a guide for the focus group, which outlines the topics you want to cover and the order in which you want to cover them.
- Encourage participants to share their experiences and feelings about the project.

Once you have collected data on project outcomes, you will need to analyze that data to understand the project’s impact. This can be done through quantitative or qualitative analysis or a combination of both.
Analysis of Data
We know data analysis can be a bit daunting, but there are a few things you can do to make it easier:
- Start by looking at the big picture. What are the overall trends in the data?
- Look for patterns and relationships in the data. Are there any themes that emerge?
- The data analysis process will be different depending on whether you are using quantitative or qualitative data.
If you are using quantitative data, you will likely use statistical methods to analyze your data. This can help you to understand the project’s impact by looking at changes in project outcomes over time.
The following three factors must be taken into consideration when choosing an acceptable statistical method:
- the study’s goal and purpose,
- the type and distribution of the data used,
- and the type of observations (paired or unpaired).
All types of statistical techniques used to compare means are known as parametric techniques, whereas nonparametric techniques are used to compare measures other than means, such as median, mean ranks, and proportions. Choose solid and reliable statistical analysis software!
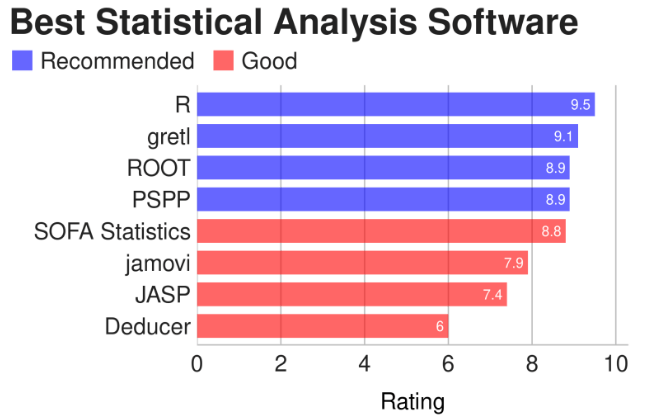
If this sounds way too complex and you don’t have someone on your team to help you out, you can always hire an outsourced data scientist to run the analysis for you!
Whereas, when you are using qualitative data, you will likely use thematic analysis to analyze your data, the process involves looking for patterns and themes in the participants’ stories. This can help you to understand how the project has affected their lives.
Thematic analysis is a method of analyzing data that focuses on identifying patterns, or themes, within the data

Tips to not forget:
- The quantitative analysis looks at changes in project outcomes over time and can be used to measure project impact.
- The qualitative analysis looks for patterns and themes in participants’ stories and can be used to understand how the project has affected their lives.
A combination of both quantitative and qualitative data can be used to get a more complete picture of project impact.
Once you have analyzed your data, you will need to communicate your findings to project stakeholders!
Communicating Findings
Loyal to the scientific method, you need to share your findings, the last step! What’s the point if you file the results? There are a lot of options to report your conclusions, such as reports, presentations, or other means.

Whatever method you choose, make sure you communicate your findings in a way that is clear and concise. Your audience should be able to understand the findings and see the project’s impact.
When communicating your findings, it is important to:
- Present the data in a visually appealing way
- Use charts, graphs, and tables to present quantitative data
- Use quotes and stories to present qualitative data
- Be clear and concise in your writing
- Focus on the project’s impact rather than project outcomes
If you are running a long-term project, take into account that this process needs to start over at some point. Your project will change over time as well as your objectives and goals.
Closing Thoughts
To sum it up, project impact measurement is the process of understanding how your project has affected the lives of those it was intended to help. It is important to collect data on project outcomes and use both quantitative and qualitative analysis to understand the project’s impact. Once you have analyzed your data, you should communicate your findings to project stakeholders and beneficiaries.
By following the tips in this article, you can ensure that your project is successful! Thank you for reading! We hope this article helped you to understand how to measure the impact of your project.
-The Monitask Team


