Remote Work Security: Risks, Strategies, and Best Practices

Remote work offers flexibility and convenience, but it also introduces new cybersecurity challenges.
Without proper safeguards, remote setups can expose businesses to cyberattacks, data breaches, and compliance risks.
Securing a distributed workforce requires proactive strategy, smart tools, and ongoing employee awareness.
Remote Work Security Threats
Remote employees operate outside corporate firewalls, often on personal devices and unsecured networks.
This decentralized environment increases the risk of security lapses.
Recognizing these risks is the first step toward building a strong defense.
Major Security Risks for Remote Workers
Remote work opens up new opportunities but also brings unique threats to data security and corporate systems.
Without proper security measures in place, the risks significantly increase. Below are the primary threats faced by remote workers and organizations:
- Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks
Phishing and social engineering are among the most common methods used by hackers to gain access to corporate systems.
In a remote work setup, employees often work without constant supervision and interaction with colleagues, which makes them more vulnerable to such attacks.
Phishing involves sending deceptive emails or messages that trick users into revealing personal data or installing malware.
Social engineering manipulates employees emotionally, persuading them to take actions that may compromise security.
- Shadow IT and Unauthorized Tools
Many remote employees use unauthorized applications and tools to perform their tasks more efficiently and conveniently.
These tools, known as Shadow IT, are often not vetted for security and may not meet corporate standards for data protection.
When these tools are used, data can be unprotected or transmitted over insecure channels, potentially leading to data breaches or access to corporate networks by unauthorized individuals.
- Personal Devices and BYOD Risks
The Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) practice, where employees use their personal devices for work, increases security risks.
Personal devices may lack proper protection, may not be updated regularly, or may lack the necessary security features.
Additionally, managing corporate data on personal devices can be challenging, especially if employees use different operating systems or devices.
This makes it difficult to ensure the security of sensitive corporate information.

- Physical Security Limitations in Home Offices
Unlike corporate offices, home offices are not typically set up for secure handling of confidential information.
Work devices can be stolen or damaged, especially if they aren’t physically secured (e.g., not locked away).
Furthermore, family members, friends, or other outsiders might accidentally gain access to work-related data, making security even more vulnerable.
- Unsecured Wi-Fi and Public Networks
Many employees work from cafés, public places, or at home, connecting to Wi-Fi networks that are not always properly secured.
These networks can be susceptible to “man-in-the-middle” attacks, where attackers intercept the data being transmitted over the network.
This increases the risk of data leakage, especially if unsecured connections are used to transmit sensitive corporate data.
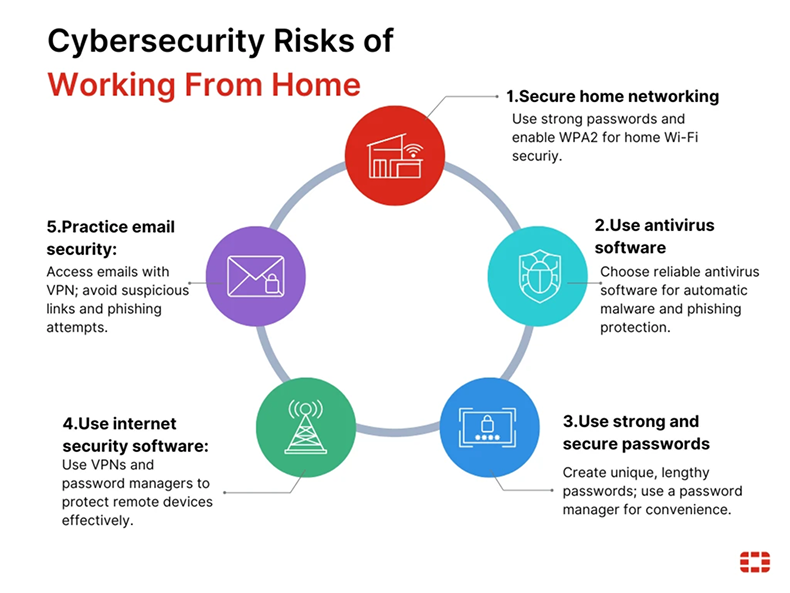
Technical Vulnerabilities to Address
As more employees work remotely, companies face new technical vulnerabilities that need to be addressed in order to safeguard sensitive data and maintain the integrity of their networks.
These vulnerabilities can arise from outdated software, insecure connections, or improperly configured devices.
Below are the critical technical weaknesses that need attention in a remote work environment:
VPN Vulnerabilities and the Need for Secure Connections
While VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) are essential for providing secure connections when employees access company networks remotely, they come with their own set of vulnerabilities.
Outdated VPN software, weak encryption protocols, and poorly configured VPN settings can leave data exposed to hackers.
As remote work becomes more widespread, it is crucial that companies ensure their VPN systems are up-to-date and use strong encryption protocols to prevent unauthorized access.
Steps to ensure secure VPN usage:
✅ Regularly update VPN software and ensure patches are applied.
✅ Enforce strong encryption standards (e.g., AES-256) for secure data transmission.
✅ Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for VPN access to reduce unauthorized entry.
Unpatched Software and Outdated Systems
Another significant vulnerability in remote work environments is the use of unpatched software or outdated operating systems.
Cybercriminals frequently exploit vulnerabilities in software that has not been updated with the latest security patches.
When remote employees are using outdated systems or unpatched applications, they become easy targets for malware, ransomware, or other types of cyber-attacks.
Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that all devices, software, and applications used by remote employees are consistently updated with the latest patches.
How to mitigate risks from unpatched software:
✅ Regularly schedule software updates and patches for all devices, especially operating systems and critical applications.
✅ Use automated patch management tools to ensure timely updates across all devices.
✅ Ensure employees are educated about the importance of maintaining up-to-date systems and software.
Maximize productivity of your business
Track employee productivity and simplify work with them
Endpoint Vulnerabilities in Remote Work Devices
Remote work involves using personal or company-issued devices outside of the secure office environment.
These devices, whether laptops, smartphones, or tablets, may have vulnerabilities that can be exploited if not properly secured.
Endpoint protection is essential to defend against malware, phishing attacks, and other threats that target these devices.
Endpoint security tools like antivirus software, firewalls, and device encryption are necessary to ensure that remote devices are adequately protected.
Key measures for securing remote work endpoints:
✅ Install and update antivirus and anti-malware software on all devices.
✅ Enforce device encryption to protect data in case of loss or theft.
✅ Use endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools to monitor and respond to security threats on remote devices.
By addressing these technical vulnerabilities and applying best practices for VPN security, software updates, and endpoint protection, organizations can significantly reduce the risks associated with remote work.
Cybersecurity in a remote work setup requires continuous monitoring, proactive security measures, and ongoing training to ensure that both employees and their devices are secure.
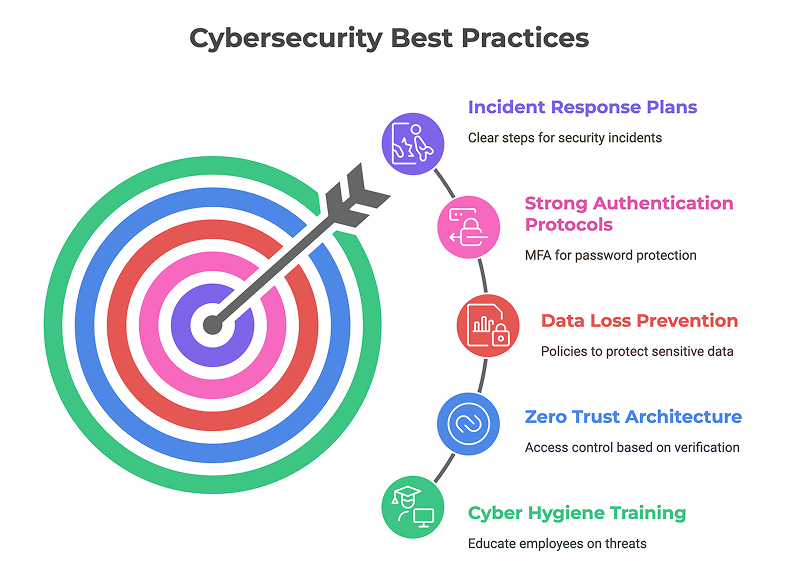
Protecting Sensitive Information
Sensitive company data should always be encrypted — both in transit and at rest.
Access control should be based on the principle of least privilege, giving employees only the data they need.
Secure file-sharing tools and watermarked documents can further reduce the risk of leaks.
Device Security and Maintenance
Remote devices must be updated regularly, with security patches applied automatically where possible.
Companies should enable features like screen locking, password enforcement, and the ability to remotely wipe or disable lost or stolen devices.
Conclusion
As remote work continues to grow, so do the associated security risks. But with the right strategies, tools, and employee education, organizations can build a resilient, secure remote work environment.
By addressing vulnerabilities proactively and fostering a culture of security, businesses can protect both their data and their people — no matter where they work from.
Security isn’t just a technical issue — it’s a daily habit. And it’s the foundation of any productive remote team!
– The Monitask Team
Frequently Asked Questions
How can organizations secure remote work environments?
Organizations can secure remote work environments by implementing robust security policies, using secure communication channels (like VPNs), enforcing multi-factor authentication (MFA), ensuring regular software updates, and providing employees with proper training on cybersecurity best practices.
Why is VPN security important for remote work?
VPNs are crucial for remote work as they provide secure connections between remote workers and company networks. However, VPN vulnerabilities, such as outdated software and weak encryption, can expose data to unauthorized access. It’s essential to use strong encryption standards and keep VPN software updated to ensure security.